Kegels Guide for Men
Arnold Kegel originally introduced the Kegel exercise in 1948 for women who experienced incontinence after giving birth. However, it was later discovered that it is also beneficial for men when it comes to strengthening the muscles in the pelvic floor.
Benefits
- Improve urinary control.
- Have stronger erections.
- Experience more intense orgasms that last longer.
- Last longer in bed.
- Good training for orgasms without ejaculation.
- Eliminate climacturia (urination while ejaculating).
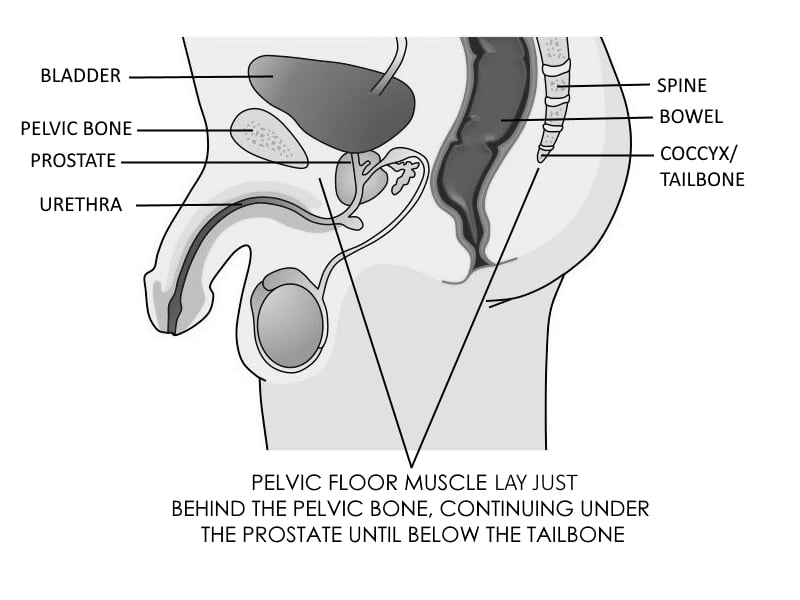
The Pelvic Floor Muscles
These are the 3 main muscles that are important during a Kegel: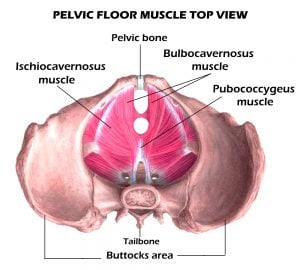
- Bulbocavernosus muscle (BC) – This muscle is located at the base of the penis and is responsible for controlling ejaculation, as well as pushing more blood into the penis. Exercising the BC muscle will encourage a larger erection and delayed ejaculation.
- Pubococcygeus muscle (PC) – PC muscle is a larger muscle that starts from the pubic bone and stretches to the tailbone. This is the muscle that contracts during orgasm. When trained properly, PC can help strengthen stamina. It also makes multiple orgasms in men possible.
- Ischiocavernous muscle (IC) – This muscle is located just beside the BC muscle. IC muscle can stabilize the penis and maintain a longer erection.
Ways to Find the Right Muscles
- Use your fingers. Lie on your back and pull your knees up. Use one or two fingers by placing them in the skin between your anus and testicles. Imagine you are stopping yourself from peeing. You should feel the movement of your pubococcygeus muscle where you placed your fingers.
- Contracting your anus. Another way of identifying the pelvic floor muscle is by tightening the muscles that stop you from passing gas. Try pulling, or lifting your anus in. While doing that, you will feel a part of your pubococcygeus muscle tightening.
- Shortening your penis. This technique requires standing in front of the mirror naked. Try lifting your testicles without using your hands. When doing this, you will notice that your penis is also being pulled up, or “shortened”. This will also cause your pelvic floor muscles to tighten.
- Stopping your urination in midstream. When you are still having a hard time locating your pelvic floor muscles after trying the three techniques above, try to stop your urination while in the middle of it. You will feel a contraction right in the middle of your testicles and the anus. Note that this activity is only for you to find the correct muscles. Do not do the actual exercise while urinating as it may cause a bladder infection.
When you find the correct muscles, you will experience the full benefits of Kegel exercise.
Steps to Perform a Kegel
- Tighten the muscles in your pelvic floor area. Make sure you are focused on the pelvic floor muscles only. Do not flex the muscles in your buttocks, abdomen, or thigh area.
- Hold that position for 3 seconds without holding your breath. It is best to breathe freely while holding the contraction.
- Relax your muscles for 3 seconds.
- Repeat 10 times and do this at least three times a day.
When you perfect this technique and feel that your pelvic floor is getting stronger, try doing the exercise while sitting, walking or standing.
At first, it will be easier to do Kegel exercises while lying down, but practicing Kegel exercises regularly can help you do them anytime, anywhere.
Three Kegel Techniques
- Contract the muscles for four seconds, relax for two seconds, and then repeat five times in a row.
- Contract and relax quickly ten times.
- Tighten for ten seconds, relax for five seconds, and then repeat 5 times in a row.
Whenever you feel like these exercises are getting easier, you can increase the duration of the contraction. It is important to try all of the three techniques as one of them may best train you to have multiple orgasms and overcome premature ejaculation.
Safety Precaution
- Discontinue your Kegel routine when you notice you are having a hard time getting or maintaining an erection. This is also recommended when you feel sore or tense during the exercise. Sometimes, these are signs that you have overdone your Kegels or you did not do them correctly. Rest for at least one week, and start again when the problem resolves.
- Don’t tighten your muscles too tight. The contractions should not take serious efforts to the point of feeling uncomfortable.
- Don’t hold the contraction for too long. You should be able to relax the muscles in between contractions. The goal of pelvic floor exercises is to train you to be able to tighten the correct muscles and relax them at will.
Best Times to do Kegels
- Fit in one set of your Kegel exercises with your daily routines. For Example, when you are brushing your teeth or waiting in line.
- It is recommended to do a set of Kegels after urinating to encourage the last drops of urine to come out.
- Try to tighten your pelvic floor muscles before any activity that pressures your abdomen area. For example, coughing, heavy lifting, laughing, or sneezing.
When to See Results
|
Health Issue |
When to see the full result after regular therapy |
|---|---|
|
Fecal/urinary incontinence |
3 – 6 weeks |
|
Post-void dribbling (leaking of urine after urinating) |
3 – 6 weeks |
|
Erectile dysfunction |
15 months |
|
Premature ejaculation |
2 – 8 months |
Side Effects
Some men have reported abdominal and chest pain after starting the Kegel exercises. However, these side effects are results of not doing the exercise properly.
Kegel is completely harmless when done correctly. Sometimes, simple factors such as holding your breath while doing the exercise can lessen the effectiveness of this therapy.
Medical Procedures That Help
Some men may realize that the Kegel exercises don’t work. This may be because of not being able to find the correct muscle. The doctor may perform any of these procedures to help you determine if you are contracting the correct muscles.
- Biofeedback – A process where a doctor will insert a probe into the rectum. The doctor will encourage the patient to tighten and relax the pelvic floor muscle to monitor the muscle activity. The exerciser will then let you know if you are contracting the correct muscles.
- Ultrasound – An ultrasound probe will be placed below the scrotum, just in front of the anus. Alternatively, the evaluator may place the probe on the abdomen.0